- Plant-Based Protein
- Natural Plant Flavours
- Food and Dietary Supplement Ingredients
- Fruit Juice Powder
- Animal Nutrition Ingredients
- Water Soluble Ingredients
- Cosmetic Ingredients
- Unveiling the Therapeutic Potential of Rabdosia Rubescens: A Comprehensive Review
- What are the medicinal properties of Rabdosia Rubescens?
- Nutritional value of Orange Juice Powder compared to fresh orange juice.
- Processing Conditions and Nutritional Value of Orange Juice Powder
- Exploring the Versatility of Herbal Extracts in Food Flavors

What are the health benefits of hawthorn leaf?
Welcome to our blog! Today, we are diving into the world of hawthorn leaf and uncovering its incredible health benefits. Whether you're a fan of herbal remedies or simply curious about natural alternatives, hawthorn leaf is definitely worth exploring.


Nattokinase and benefits,side effect, uses,dosage
Nattokinase is an enzyme extracted from natto, made from fermented soybeans.The only source of nattokinase is from natto. Nattokinase is believed to benefit people with heart and vascular diseases, in part by breaking down blood clots that can impede circulation. While generally considered safe and tolerable.
Nattokinase and benefits,side effect, uses,dosage | Health for Circulation
Nattokinase, also known as natto extract.Nattokinase is an enzyme extracted from natto, made from fermented soybeans.The only source of nattokinase is from natto. Nattokinase is believed to benefit people with heart and vascular diseases, in part by breaking down blood clots that can impede circulation. While generally considered safe and tolerable.
What you may get from us: If you're developing a product that contains nattokinase or natto extract .I think you can find the information or products you need here.
Production process: Nattokinase is an enzyme extracted from natto, a food made from fermented soybeans. To make natto, boiled soybeans are combined with the bacteria Bacillus subtilis natto. Nattokinase is then distilled and purified from natto.
How to use Natto extract/Nattokinase powder: What you need is just use our products to formulate your products. It can be mixed with your other ingredients directly to make premix products. It can also be directly used for filling capsules or making tablets. Easy to say, our products are ready for Formula products.
|
Specification informations for the products |
||
|
Nattokinase/ Natto Extract powder |
||
|
Appearance |
Fine powder |
|
|
Color |
Off white or light Yellow. |
|
|
Purity of active compunds |
5000FU/g, 12000FU/g , 20000FU/g |
By UV |
|
Molecular Weight: |
27.7KD |
|
|
VK2 |
<10ppm |
|
|
Other parameter |
We also control other parameters like: moisture, Microbiological limits, Heavy metals. |
|
|
Packing type and size |
25 kg per paper drum |
|
|
For pricing or more information, please call 86 29 88444632 or send an email to Sales@nutraherbsource.com
|
||
Overview Information:
Common Name(s): Flite Tabs, Natto-K, Natto, NattoMax, Natural Super Kinase – Spray Dried(NSK-SD), Vein Caps, Cardiokinase, Fermented soybeans, Nattokinase, Subtilisin NAT, Subtilisin natto
Description:
Nattokinase is an enzyme (a protein that speeds up reactions in the body) that is extracted from a popular Japanese food called natto. Natto is boiled soybeans that have been fermented with a type of bacteria.
Natto has been used as a folk remedy for diseases of the heart and blood vessels for hundreds of years. But you won’t find nattokinase in soy foods other than natto, since nattokinase is produced through the specific fermentation process used to make natto.
Mechanisms of Action
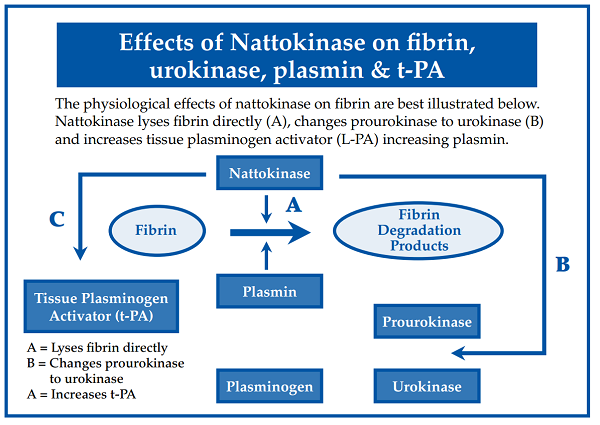
Despite its name, nattokinase is not a kinase enzyme but instead belongs to the serine protease family of enzymes, which work to break down other proteins. The mechanisms of action studied in animals or human cells, are as follows. Nattokinase:
· Directly dissolves cross-linked fibrin
· Increases release of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) from cells, which also breaks down fibrin
· Increases urokinase levels by converting internal prourokinase to urokinase. More of this enzyme will lead to more plasmin in the blood, which is responsible for degrading fibrin
· Inactivates plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). PAI-1 inhibits plasmin formation, which, as mentioned above, degrades fibrin
· Inhibits platelet aggregation by blocking thromboxane (a substance released from platelets that causes blood clotting and blood vessel constriction) formation
Health Benefits of Nattokinase
1) May Decrease Blood Pressure
Nattokinase inhibits the angiotensin-converting enzyme, which causes narrowing of blood vessels. Inhibiting this enzyme may be involved in reducing blood pressure.
In 2 clinical trials, one with 79 and the other with 86 subjects with high blood pressure, the group which received a dose of nattokinase once a day for 8 weeks had reduced blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) compared to the placebo group. One of the studies found the reduction in blood pressure was more significant in male subjects.
2) Nattokinase May Prevent Blood Clots
Nattokinase has the potential to be a treatment for thrombosis (formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel).
In a clinical trial, 45 subjects were divided into 3 groups and received nattokinase daily for 2 months: a healthy group, patients at the risk of heart disease, and patients undergoing dialysis. Risk factors for heart disease (fibrinogen, factor VII, and factor VIII) significantly decreased in all groups.
In a study of 12 healthy adult males, a single dose of nattokinase degraded fibrin and decreased levels of coagulation factors, which are involved in blood clotting. Its effect lasted for a long time (over 8 hours) compared to other enzymes (tissue plasminogen activator, urokinase).
In rats, its clot-dissolving activity was stronger than that of plasmin or elastase.
In rats with thrombosis, nattokinase decreased blood clots better than the saltwater solution. In addition, a high-dose of nattokinase was as effective in reducing blood clots as a known anti-clotting agent (vermis kinase).
Studies in human cells suggest that nattokinase:
· Directly reduces fibrin clots 6 times more efficiently than plasmin
· Increases activity of anti-clotting enzymes (urokinase, t-PA)
· Reduces pro-clotting enzymes (PAI-1)
3) May Improve Blood Flow
Nattokinase improves blood flow by inhibiting blood cell clumping (platelet aggregation) and thrombus formation.
In rats, a high dose of nattokinase fully inhibited thrombus formation. This was similar to the effects of aspirin, a well-known blood thinner. Nevertheless, the lack of adverse effects associated with its consumption suggests that it could be an effective treatment for improving blood flow.
Blood clots were experimentally induced in dogs. Oral consumption of nattokinase dissolved the blood clots and restored normal blood flow in only 5 hours.
4) May Reduce Cholesterol
A study comparing nattokinase with statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs) randomly divided 82 patients into one of those treatments for 26 weeks. Both treatments reduced total cholesterol, LDL (the “bad” cholesterol), and triglycerides. However, only nattokinase consumption increased HDL (the “good” cholesterol).
Other studies do not report a significant reduction in cholesterol levels or only showed a decrease in triglycerides levels. Hence, further studies are required to examine its effect on cholesterol levels.
5) May Prevent Artery Hardening
Daily nattokinase supplementation was remarkably better at reducing plaque size (36.6% plaque reduction) that causes hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) compared to statin treatment (11.5% plaque reduction) in 82 patients. The mechanisms by which it reduces cholesterol levels and decreases plaque size that results in the prevention of artery hardening may be different from each other.
6) May Decrease Risk of Stroke
High von Willebrand Factor (vWF, a mediator released by damaged blood vessels that increases the risk of forming clots) levels are associated with the risk of stroke.
In a study of 79 hypertensive patients, vWF was reduced by 15% in the group who took nattokinase, compared to the placebo group that had no consistent change throughout the 8 weeks. However, vWF levels didn’t decrease in males who consumed the supplement. This suggests a gender-specific effect of nattokinase in reducing vWF levels.
7) May Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
In rats, nattokinase helped control factors that characterize Alzheimer’s disease.
Certain factors that are high in Alzheimer’s decreased with oral nattokinase consumption (acetylcholinesterase, TGF-β, Fas, and IL-6). Meanwhile, others that are usually low, increased with nattokinase treatment (BDNF and IGF-1) compared to untreated rats with Alzheimer’s disease characteristics. Thus, nattokinase may be a potential therapy for the treatment of Alzheimer’s.
In cells, it also degrades amyloid fibrils, which are protein aggregates commonly found in cases of Alzheimer’s disease.
8) May Treat Celiac Disease
In cells, nattokinase efficiently degraded parts of gliadin, a component of gluten. Hence, it may be a potential new treatment for intolerance to gliadin, known as celiac disease.
Note: Many benefits of nattokinase were studied in cells or animals. Even though the findings were significant, these benefits may or may not apply to humans. For this reason, It’s better to do studies in humans if needed.
Possible Side Effects
As a derivative of nattō, a food eaten for centuries in Japan, nattokinase is presumed to be safe, although there is little data as to its long-term effect. That doesn't mean that it is without concerns.
Because nattokinase can influence blood circulation and chemistry, it should be used with caution in certain groups, namely:
· People with bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, in whom nattokinase may make symptoms worse
· People who take blood thinners, including warfarin, in whom nattokinase may promote bleeding and easy bruising
· People with low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, in whom nattokinase may cause lightheadedness, headaches, dizziness, and fainting
· People on antihypertensive drugs, like ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers, in whom nattokinase may intensify the drug's effect, triggering hypotension
Nattokinase should also be stopped no less than two weeks prior to a scheduled surgery to reduce the risk of excessive bleeding.
Daily Recommended dosage.
Nattokinase daily value: 3000fibrin units (FU) to 5000fu.
- Prev:Pomegranate Extract(Punicalagins) and benefits,side effect, uses,dosage
- Next:Fenugreek Seed Extract,Furostanol saponins and Health benefits, uses Improve testosterone











