- Plant-Based Protein
- Natural Plant Flavours
- Food and Dietary Supplement Ingredients
- Fruit Juice Powder
- Animal Nutrition Ingredients
- Water Soluble Ingredients
- Cosmetic Ingredients
- Unveiling the Therapeutic Potential of Rabdosia Rubescens: A Comprehensive Review
- What are the medicinal properties of Rabdosia Rubescens?
- Nutritional value of Orange Juice Powder compared to fresh orange juice.
- Processing Conditions and Nutritional Value of Orange Juice Powder
- Exploring the Versatility of Herbal Extracts in Food Flavors

What are the health benefits of hawthorn leaf?
Welcome to our blog! Today, we are diving into the world of hawthorn leaf and uncovering its incredible health benefits. Whether you're a fan of herbal remedies or simply curious about natural alternatives, hawthorn leaf is definitely worth exploring.
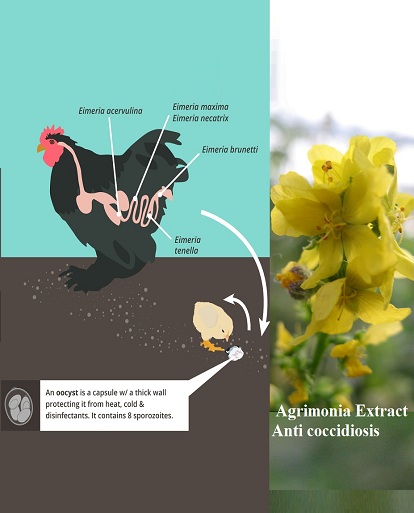

Agrimonia Extract, Avian disease,Antibacterial, Antidiarrheal,Anticoccidiosis in poultry industry
Components of Agrimonia species have been reported as candidate antimicrobials that possess antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties. Agrimonia has a strong antiviral and antiviral effect, which can be widely used in the treatment of avian influenza and domestic cold and fever. Agrimonia is effective against many parasites and can be used to drive away parasites and pathogenic protozoe in poultry and livestock, such as coccidiosis caused by Eimeria. And it can treat the symptoms of fecal blood and diarrhea caused by coccidiosis, effectively improve the feed conversion rate of birds, and make birds gain higher weight.In the international situation of total prohibition of antibiotics, Agrimonia can be used as an alternative to antibiotics.
Background
Avian influenza refers to the disease caused by infection with avian (bird) influenza (flu) Type A viruses. These viruses occur naturally among wild aquatic birds worldwide and can infect domestic poultry and other bird and animal species.
Parasitoses represent a limiting factor in the breeding of poultry species, both in high-production commercial rearing farms or even in rustic breeding systems, where economic losses can be significant. Among the most pathogenic parasites, coccidiosis caused by Eimeria spp. is distinguished by severe enteropathy, which promotes anorexia, decreased reproduction and posture in adults, and is responsible for high levels of mortality in young animals.
In the past, antibiotics or chemicals were mainly used to treat poultry parasites or influenza diseases.
Because antibiotic use in livestock is assumed to contribute to the emerging public health crisis of antibiotic resistance, alternatives are required. Phytogenic additives are extensively studied due to their antibiotic properties.
In European countries, the prophylactic use of anticoccidial chemicals as feed additives has been strictly limited since 2006 and a full ban has been proposed to be effective in 2021 (Council Directive of 2011/50/EU of the European Council). Natural products are emerging as an attractive way to combat coccidiosis.In the international situation of total prohibition of antibiotics, Agrimonia can be used as an alternative to antibiotics.

What you may get from us: If you're developing a product that contains plant active ingredients from Agrimonia eupatoria or Agrimonia pilosa.I think you can find the information or products you need here.
Simple production process in our factory: After the plant is collected, raw material will be processed by solvent extraction, separation and purification, filtration, concentration, drying and other steps to form the final products. We may also design a prouction process based on your special requirements.
Through the physical and chemical processes, those compunds you don't want was removed, and the compunds preferred was accumulated. Which make the products achieve the best effects.
|
Agrimonia Standardized Extract |
||
|
Appearance |
Powder |
|
|
Color |
Brown |
|
|
Partical size |
Normally pass through 80mesh |
|
|
Pack size |
25 kg per paper drum |
|
|
Purity of active compunds |
5% Phenolic Compounds |
By UV |
|
For pricing or more information, please call 86 29 88444632 or send an email to Sales@nutraherbsource.com. |
||
What is Agrimony?
Agrimonia commonly known as agrimony, is an erect, perennial herb, up to 100 cm high, mostly unbranched, with a cylindrical stem. The pinnate leaves are serrated and covered with soft hairs. Flowers are hermaphrodite with 5 yellow petals, arranged on slender, terminal spikes. The fruit is surrounded by several rows of soft, hook-shaped bristles.
Botanical Source:Agrimonia eupatoria, Agrimonia pilosa
Synonyms: Common Agrimony. Church Steeples. Cockeburr. Sticklewort. Philanthropos.

Chemical constituents
The phytochemical analysis of the aerial parts of the plant revealed the presence of carbohydrates, tannins, terpenoids, phenolic compounds (flavonoids), agrimony, agrimony lactone, glycosides and oils. Aerial parts werealso contained 3% to 21% condensed tannins, polysaccharides, triterpenoid ( α-amyrin, ursolic acid, euscapic acid), silicic acid, salicylic acid, traces of essential oil, flavonoids, organic acids, ascorbic acid, nicotinamide complex (about 100-300 pg/g leaf), thiamine (about 2µg/g leaf) and vitamin K. The fresh herb contained agrimoniolide, palmitic and stearic acids, ceryl alcohol, phytosterols and volatile oil 0.2%. Seeds contained oil consisted of oleic, linoleic and linolenic acids. The volatile constituents in the root and leaf of Agrimonia eupatoria were included (% of the total): �-Pinene 8.31, Hexanal 0.05, �-Pinene 1.27, Camphene 3.21, 3-Octanol 0.27, Cymene 0.18 , D-Limonene 1.29,Eucalyptol 3.26, �-trans-Ocimene 0.51, Linalool 5.72, �-Campholenal 0.72, L-Camphor 2.11, Borneol 0.07, 4-Terpineol 1.47, �-Terpineol 4.21, p-Menth-1-en-4-ol 0.06, Pulegone 0.17, 3,4-Dimethylbenzaldehyde 0.41, 2,4-Dimethylbenzaldehyde 0.72, 2-Cyclopropylidene1,7,7-trimethyl-bicyolo [2,2,1] heptane 0.52, 1-(2-Furyl)-1-hexanone 4.87, Bergamot oil 1.42, Nonanoic acid 0.06, 2-Methyl-4-hydroxyacetophenone 0.10, Thymol 0.82, Carvacrol 0.44, Anethole 0.07, Bornyl acetate 3.72, Neryl acetate 0.47, Geraniol acetate 0.61, Furan,2,5-dibutyl 0.04, Decanoic acid 0.06, Eugenol methyl ether 0.52, �-Cedrene 2.87, �-Longipinene 1.42, Caryophyllene 0.81, �-Cedrene 0.14, Geranyl acetone 0.84, Copaene 0.05, Longofolene 0.11, Aromadendrene 0.42, Curcumene 0.72, �-Selinene 0.92, �-Selinene 0.47, �-Guaiene 0.61, �-Himachalene 0.13, �-Bisabolene 0.42, Acoradiene 0.23, �-Cadinene 0.43, Cuparene 0.37, Myristicin 0.45, �-Guaiene 0.09, transNerolidol 0.22, e-Cadinene 0.92, Caryophyllene oxide 0.58, �-Cadinene 1.53, Cedrol 14.37, epi-Cedrol 1.15, Muurolol 0.46, �-Cadinol 1.43, Patchoulol 2.17, Epiglobulol 0.08, Cubenol 0.72, Cedryl acetate 0.76, Torreyol 0.38, Farnesyl acetate 1.73, �-Eudesmol 0.06 and 14-Trimethyl-2-pentadecanone 1.24. Flavonoid content of common Agrimony herb ranged from 1.22% to 1.40%. The flavonoids extracted from the plant were differ according to the source of the plant, Lee et al., isolated ten flavonoids including kaempferol 3-O- -D-(200 - Oacetyl)glucopyranoside, tiliroside, astragalin, apigenin 7-O--D-glucuronide, rutin, iso- quercitrin, quercitrin, luteolin 7-O- -D-glucur- onide, and luteolin 7-O- -D-glucopyranoside. However, the phenols isolated by Zhang et al., were included: apigenin-7-O-3-D-glucopyranoside, catechin, quercetin, rutin, kaempferol-3-O-alpha-L-rhamnoside, Kampferol-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, lutcolin-7-O-betaD-glucopyranoside, 19alpha, 24-dihydroxy ursolic acid, 3,3'-di-O-mcthyl ellagic acid4-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside . While, Correıa et al., isolated flavan-3-ols (catechin and procyanidins B1, B2, B3, B6, B7, C1, C2 and epicatechin-epicatechin-catechin), quercetin 3-O-glucoside, quercetin 3-O-galactoside, kaempferol 3-O-glucoside, kaempferol 3-O-(6''-O-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside, apigenin 6-C-glucoside. Shabana et al,. found that the plant
contained tannins (10.08%), flavonoids (0.33%) and phenolic acids (2.26%) (luteolin 7-O-sophoroside, luteolin 7-O (6"- acetylglucoside), acacetin 7-O-glucoside, luteolin 7-O-glucoside and apigenin 7-O-glucosidep, protocatechuic, vanillic acids, p-hydroxybenzoic acid).
Antioxidative potential of Agrimonia eupatoria L
In folk medicine Agrimonia eupatoria (Agrimony) is well known with its beneficial effects in various diseases. Based on its use, studies on aqueous and aqueous-alcoholic extracts are directed on elucidating of the antioxidant, antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory activity. We have shown that antioxidant activity of Agrimony is associated with high polyphenolic content, and the extracts modified the expression of pro-inflammatory factors and enzymes from glutathione metabolism in cell culture and animal models. Administration of extracts prevented body mass gain and fat accumulation and normalized serum lipid profile in high fructose fed rats. The herb is shown to be a perspective therapeutic especially for treatment of social significant diseases such as diabetes and obesity, accompanied by low-grade inflammation.
Application scope
The most impressive health benefits of agrimony include its ability to reduce inflammation, improve digestive functions, improve bladder control, antibacterial, antivirus,antidiarrheal,anti-parasites.
Control parasites in Poultry
Agrimonia pilosula can drive away the parasites in the chicken population and treat yellow and white dysentery. It's better to deworming once in about 50 days for chickens, not for broilers with short growth cycle, and once before laying. When there are crystals similar to rice meal in the feces of chickens, they belong to parasite eggs, so they should be repelled.
Cure Bird flue
Agrimonia can reduce fever, and Agrimonia can enhance the effect of reducing fever when chickens have a cold. The fever of chicken group showed that the mental state was not good, the feed intake decreased, and the root of chicken wing felt hot.
Pharmacological effects
Antibacterial effect
Marked antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and α-haemolytic Streptococci has been reported for Agrimony. Aqueous extracts inhibited Mycobacterium tuberculosis, including the strains resistant to streptomycin and p-aminosalicylate. Essential oil was antibacterial, it was active against Bacillus subtilis.
The antibacterial (against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli) and wound healing effects of the extracts of Agrimonia eupatoria (aqueous and ethanolic) were studied. The results showed that the ethanolic extract was more effective on inhibiting the tested bacteria than the aqueous extract. P. aeruginosa was the most resistant bacteria, while highest inhibition zone appeared against E. coli (20 mm). There was a moderate activity agains S. aureus with inhibition zone of 15 mm.
Preparations of Agrimonia eupatoria were screened for antimicrobial activity against selected Grampositive and Gram-negative bacteria of relevance in wounds using a 96 well plate microdilution method (200, 40 and 8μg/ml). It exerted moderate antibacterial effects.
Antiviral effect
Ethanolic extract of Agrimonia eupatoria was reported to be active against Columbia SK virus. The Inhibitory activity of an aqueous extract of the aerial parts (stems and leaves) of Agrimonia eupatoria against hepatitis B virus (HBV) was investigated. The extract prepared at 60 degrees ºC was found to have the greatest effect. The inhibitory activity of Agrimonia eupatoria extracts on HBsAg secretion varied over the growing season and was the highest at mid-July. This inhibitory activity suggest that Agrimonia eupatoria contain potential antiviral activity against HBV.
Broad-spectrum antiviral effect of Agrimonia extract on influenza viruses.
Influenza virus continues to emerge and re-emerge, posing new threats for humans. extract of Agrimonia pilosa was shown to be highly effective against all three subtypes of human influenza viruses including H1N1 and H3N2 influenza A subtypes and influenza B virus. The EC(50) value against influenza A virus, as tested by the plaque reduction assay on MDCK cells, was 14-23 microg/ml. The extract also exhibited a virucidal effect at a concentration of 160-570 ng/ml against influenza A and B viruses when the viruses were treated with the extract prior to plaque assay. In addition, when tested in embryonated chicken eggs the extract exhibited a strong inhibitory effect in ovo on the H9N2 avian influenza virus at a concentration of 280 ng/ml. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis data showed that the extract, to some degree, suppressed viral RNA synthesis in MDCK cells. HI and inhibition of neuraminidase were observed only at high concentrations of the Agrimonia pilosa extract. And yet, Agrimonia pilosa extract's antiviral activity required direct contact between it and the virus, suggesting that its antiviral action is mediated by the viral membrane, but does not involve the two major surface antigens, HA and NA, of the virus. The broad-spectrum antiviral activity of Agrimonia pilosa extract on various subtypes of influenza viruses merits further investigation as it may provide a means of managing avian influenza infections in poultry farms and potential avian-human transmission.
Wound healing effect
The antibacterial activity of some extracts of Agrimonia eupatoria (aqueous and ethanolic) against some pathogenic bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli) and their activity on wound healing in rats , also the presence of some active compounds in both extracts were detected. The results showed that the ethanolic extract was more effective on inhibiting tested bacteria than the aqueous extract. P.aeruginosa was the most resistant bacteria, while highest inhibition zone appeared on E.coli (20 mm) .There was a moderate activity against S.aureus with inhibition zone 15 mm. by using ethanolic extract (10 mg/ml). The phytochemical analysis for detection of active compounds revealed the presence of Carbohydrates, Glycosides and Tannins in both extracts, while some of compounds such as Terpenoids and Phenolic compounds (flavonoids) were detected in the ethanolic but not in the aqueous extracts. Prepared ethanolic extract ointment showed wound healing activity in rats in contrast with fucidin ointment and aqueous extract ointment, hence the wound healing was completed in l0 days by using the ethanolic extract ointment, while the healing was completed in 12 and 14 days for the aqueous extract and fucidin ointments respectively, while, the untreated wound needed more than 16 days for healing completion.
Immunomodulatory effect
An aqueous ethanol extract of the herb was tested for immunomodulative activity in the peritoneal cavities of mice. They produced immunostimulant activity resulted in an increase in phagocytic activity and increases in the activities of lysozyme and peroxidase.
Gastrointestinal effect
A compound herb preparation containing Agrimony has been used to treat 35 patients suffering from chronic gastroduodenitis. After 25 days of therapy, 75% of patients claimed to be free from pain, 95% from dyspeptic symptoms and 76% from palpitation pains. Gastroscopy indicated that previous erosion and haemorrhagic mucous changes had healed.
AntiDiarrhea effect
Agrimony’s anti-inflammatory benefits make it useful for treating a variety of gastrointestinal ailments that include diarrhea.
Agrimonia pilosula has a bitter taste and is dry and wet. It can remove the heat and dampness of large intestine and stop dysentery. Agrimony can be taken by decocting in water alone or with other dysentery drugs. Cold in winter, the chicken group is easy to catch cold diarrhea, yellow and white diarrhea occurs in the chicken group, you can try to use this prescription. Agrimonia is bitter and astringent to stop bleeding. Cold and hot bleeding can be stopped. Intestinal bleeding of chickens, bloody stools caused by cecal coccidia and bloody feces can all be taken by Xianhecao boiled water for chickens. 30g to 60g Xianhecao can be used together with AI ye to stop bleeding. Agrimonia can solve the cough induced by influenza and respiratory diseases in chickens. Agrimonia can give you 100 parts, Platycodon grandiflorum, liquorice, pinellia, etc. together, it can reduce phlegm and cough, diminish inflammation, and calm down. Usage: decoct and take some agrimony in boiling water for four days.
Hepatoprotective effect
The hepatoprotective effects of Agrimonia eupatoria water extract (AE) was studied in chronic ethanol-induced liver injury in rats. Animals were treated orally with AE at 10, 30, 100, and 300 mg/kg/day. After chronic consumption of ethanol, serum aminotransferase activities and pro- inflammatory cytokines markedly increased, and those increases were attenuated by AE. The cytochrome P450 2E1 activity and lipid peroxidation were increased after chronic ethanol consumption, while reduced glutathione concentration was decreased. Those changes were attenuated by AE. Chronic ethanol consumption also increased the levels of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and myeloid differentiation factor 88 protein expression, inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 protein, mRNA expression, and nuclear translocation of nuclear factor- kappa B, all these effects were attenuated by AE. The results revealed that AE ameliorates chronic ethanol-induced liver injury, and that protection is likely due to the suppression of oxidative stress and TLRmediated inflammatory signaling.
- Prev:Medicinal herb-Artemisia,Antibacterial, Anticoccidiosis,Use for poultry and livestock industry
- Next:Skullcap Extract and benefits,side effect, uses,dosage











