- Plant-Based Protein
- Natural Plant Flavours
- Food and Dietary Supplement Ingredients
- Fruit Juice Powder
- Animal Nutrition Ingredients
- Water Soluble Ingredients
- Cosmetic Ingredients
- Unveiling the Therapeutic Potential of Rabdosia Rubescens: A Comprehensive Review
- What are the medicinal properties of Rabdosia Rubescens?
- Nutritional value of Orange Juice Powder compared to fresh orange juice.
- Processing Conditions and Nutritional Value of Orange Juice Powder
- Exploring the Versatility of Herbal Extracts in Food Flavors

What are the health benefits of hawthorn leaf?
Welcome to our blog! Today, we are diving into the world of hawthorn leaf and uncovering its incredible health benefits. Whether you're a fan of herbal remedies or simply curious about natural alternatives, hawthorn leaf is definitely worth exploring.
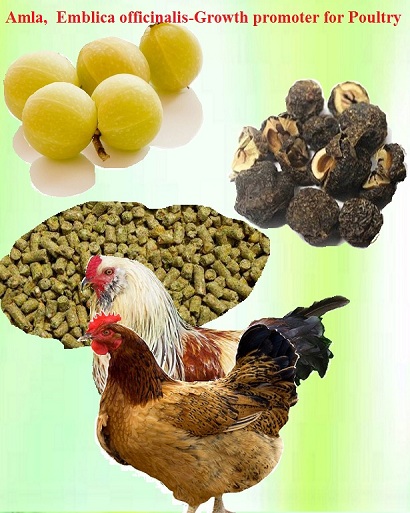


Amla,Emblica officinalis-Growth promoter in livestock and poultry
Amla (Phyllanthus emblica Linn or Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) has various medicinal applications,It has variety of phytochemical such as tannins, flavonoids, terpenoids and alkaloids,These compounds have been indicated several pharmacological properties such as carminative, digestive, stomachic, laxative, immune stimulator, antioxidant, antimicrobial and anticoccidial effects. It is considered to be safe herbal feed additives without any adverse effects.Proper use of amla as phytogenic feed additive will be efficient for poultry and livestock production. It will be a good growth promoter for animals.
Amla (Phyllanthus emblica Linn or Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) is a valuably medicinal plant. Various parts of the plant are used to treat a range of diseases or used as feed additives in animals but the most important part is fruit. The fruit is rich in quercetin, phyllaemblic compounds, gallic acid, tannins, flavonoids, pectin and vitamin C and also contains various polyphenolic compounds. A wide range of phytochemical components including terpenoids, alkaloids, flavonoids and tannins have been shown to posses useful biological activities. The fruit is used either alone or in combination with other plants and have wide range of action such as antipyretic, analgesic, antitussive, adaptogenic properties. Amla is also reported to possess radiomodulatory, chemomodulatory, chemopreventive effects, free radical scavenging, antioxidant, antiinflammatory, antimutagenic and immunomodulatory activities.
Background
Herbal feed supplement (feed additive) is a substance or mixture used in minor quantity other than basic feed in order to complement certain nutrients for improving performance of the livestock and poultry. The efficiency of poor quality roughages utilization can be maximized by the supply of deficient nutrients like nitrogen, micronutrients, feed additives etc. in the ration of animals. Growth promoters have been banned in animal nutrition. With the ban on use of antibiotics as growth promoter by European Union from March 2006, it has become need of the hour to produce drug/chemical free products. There are two principal reasons behind the changes in legislation on the use of in-feed antibiotic growth promoters. The first is to try to combat the development of microbial resistance to antibiotic drugs and its consequences on human health. The second is a response to consumer pressures to eliminate the use of all non-plant xenobiotic agents from the animal diets but at the same time, we can’t afford to compromise with the production level because of increasing demand of animal products due to increasing human population and awareness of consumer regarding the importance of animal protein. Phytochemicals contained in some medicinal herbs could act the following potential mechanisms on animal system: (i) increased feed intake (ii) improved feed efficiency (iii) improved gut function leading to reduced incidence of digestive disturbances (iv) stimulation of digestion (v) methane inhibition (vi) immune modulation (vii) antioxidant and (viii) antimicrobial effect.
Because of the properties found in amla (Phyllanthus emblica Linn or Emblica officinalis Gaertn.),it is explored as herbal feed additive to enhance the livestock and poultry production. Sometime,Amala may be mixtured with several herbs to play its function better.
What you may get from us: If you're developing a feed additive that contains medicinal herb of Amla (Phyllanthus emblica Linn or Emblica officinalis Gaertn.).I think you can find the information or products you need here.
Simple production process in our factory: After the plant is collected, It can be made straight powder. Or the raw material will be processed by solvent extraction, separation and purification, filtration, concentration, drying and other steps to form the final products. We may also design a prouction process based on your special requirements.
Through the physical and chemical processes, those compunds you don't want was removed, and the compunds preferred was accumulated. Which make the products achieve the best effects.
|
Amla Straight powder or Amla Extract |
||
|
CAS No. |
90028-28-7 |
|
|
Appearance |
Powder |
|
|
Color |
Brown |
|
|
Partical size |
Normally pass through 60mesh |
|
|
Pack size |
25 kg per paper drum |
|
|
Purity of active compunds |
20%,30%,40% Tannins |
By UV |
|
For pricing or more information, please call 86 29 88444632 or send an email to Sales@nutraherbsource.com.
|
||
General Information
Taxonomy
Family: Euphorbiaceae
Genus: Phyllanthus
Species: emblica L
Latin Name: Emblica officinalis Gaertn.
Common Name: Amla,Phyllanthus emblica Linn , Emblica officinalis Gaertn.,Gooseberry
Plant description
Emblica officinalis is a moderate sized plant, the average height being 5.5 metres; its bark is usually light brown to black, coming off in thin strips or flakes, exposing the fresh surface of a different colour underneath the older bark; the average girth of the main stem is 70 cm; in most cases, the main trunk is divided into 2 to 7 scaffolds very near the base.
Leaves, 10 to 13 mm long, 3 mm wide, closely set in pinnate fashion, making the branches feathery in general appearance. The leaves develop after the fruit-set.
Flowers, unisexual, pale green, 4 to 5 mm in length, borne in leaf-axils in clusters of 6 to 10; staminate flowers, tubular at the base, having a very small stalk, gamosepalous, having 6 lobes at the top; stamens 1 to 3, polyandrous, filaments 2 mm long; pistillate flowers, fewer, having a gamopetalous corolla arid a two-branched style; both staminate and pistillate flowers are borne on the same branch, but the staminate flowers occur towards the apices of small branches.
Fruits, fleshy, almost depressed to globose. 2.14 cm. in diameter, 5.68 g in weight, 4.92 ml in volume, primrose yellow.
The stone of the fruit, six-ribbed, splitting into three segments, each containing usually two seeds; seeds 4-5 mm long, 2 to 3 mm wide, each weighing 572 mg, 590 microlitres in volume, citron green.
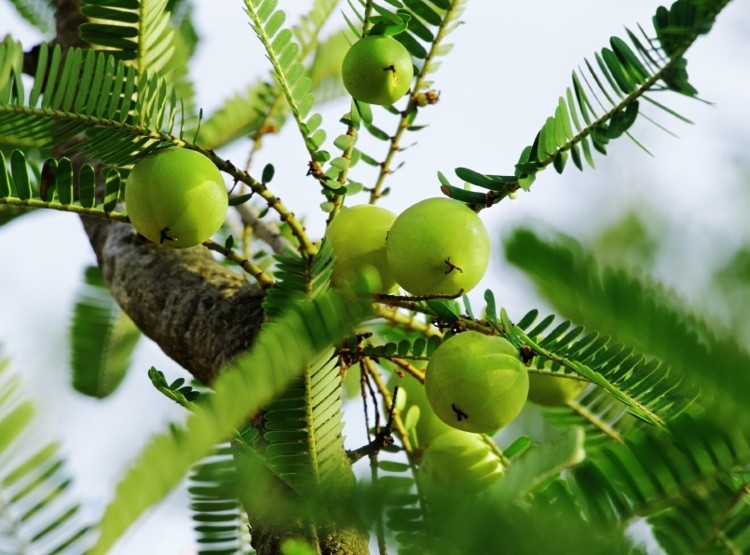

Chemical Constituents of Emblica officinalis
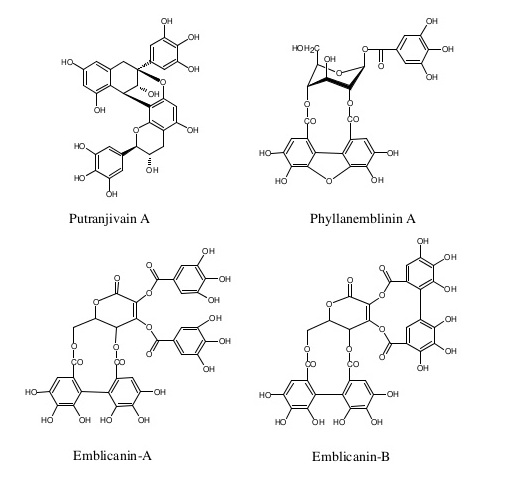
Emblica officinalis is very high in Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid), Amala is rich in quercetin, phyllaemblic compounds, gallic acid, tannins, flavonoids, pectin and vitamin C and also contains various polyphenolic compounds. A wide range of phytochemical components including terpenoids, alkaloids, flavonoids and tannins have been shown to posse’s useful biological action. The fruits, leaves and bark are rich in tannins. The root contains ellagic acid and lupeol and bark contains leucodelphinidin. The seeds yield a fixed oil (16%) which is brownish-yellow in colour. It contains linolenic acid (8.8%), linoleic acid (44.0%), oleic acid (28.4%), stearic acid (2.15%), palmitic acid (3.0%) and myristic acid (1.0%) . The phytochemicals of this plant include hydrolysable tannins (Emblicanin A, Emblicanin B, punigluconin, pedunculagin), flavonoids, alkaloids (Phyllantidine and phyllantine). Gallic acid, ellagic acid, chebulinic acid, quercetin, chebulagic acid, corilagin together with isostrictinnin, were isolated from the fruit of Phyllanthus emblica. It contains two new hydrolysable tannins with low molecular weight (<1000), called emblicanin A (37%), emblicanin B (33%), punigluconin (12%) and pedunculagin (14%) . These two new tannins (emblicanins A and B) have a very strong antioxidant action and found to preserve erythrocytes against oxidative stress induced by asbestos, generator of superoxide radical.
The health effect of Amla ( Emblica officinali) in poultry and livestock Flock
Effects on digestion
The Amla ( Emblica officinali) fruits have well known action as carminative, digestive, stomachic, laxative and tonic in nature. The regular use of Amla can strengthen digestion, absorption and assimilation of food. But it works more slowly and gently than ginger or other digestion-enhancing herbs. In addition, it improves assimilation of iron for healthy blood. Amla also strengthens the liver and helps in detoxification and removal of toxins from the body.
Amla as feed additives have no side effects on the health of birds. The dietary use of herbal growth promoter increases the performance of broiler by improving digestion, metabolism and absorption of certain nutrients which ultimately improve live weight gain and FCR. Herbs have a complex mode of action on various organs or systems due to active ingredients present in them. They are supposed to have greater impact on different factors which promote growth and health, by improving physiological and immunological functions of body. Some experiments conducted on day old broiler chicken strain to evaluate the efficacy of amla fruit on the productive performance of broiler chicken. The production was comparatively higher in amla fed group as evidence by higher body weight gain and FCR. The mortality percentage was zero in treatment groups whereas 5% mortality was recorded in control group. Likewise. Supplemented amla fruit powder in water and observed growth performance of broiler. The result showed better growth and feed utilization in treated groups as compared to control.
Gastroprotective effects
An ethanol extract of amla ( Emblica officinali) was examined for its antisecretory and antiulcer activities employing different experimental models in rats, including pylorus ligation Shay rats, indomethacin, hypothermic restraint stress induced gastric ulcer and necrotizing agents (80% ethanol, 0.2 M NaOH and 25% NaCl). Oral administration of amla extract 250 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg significantly inhibited the development of gastric lesions in all test models used. It also caused significant decrease of the pyloric-ligation induced basal gastric secretion, titratable acidity and gastric mucosal injury. Histopathological analyses are in good agreement with pharmacological and biochemical findings. The results indicate that amla extract possesses antisecretory, antiulcer and cytoprotective properties.
Antioxidant effect
As a result of metabolic reactions and diseases, there is generation of free radicals in the form of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species within the animal's body. Free radicals are chemical entities, which contains one or more unpaired electrons due to which they are highly unstable and cause damage to other molecules by extracting electrons from them in order to attain their stability. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive oxidizing agents belonging to the class of free-radicals. The free-radical initiate chain reactions by removal of an electron from another molecule to complete its own orbital. An increased production of ROS by any cell beyond the capacity of the cellular antioxidant defense leads to oxidative stress (OS), which ultimately cause significant cell damage through irreversible modification of vital cellular structures such as lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. This higher shift of oxidative stress may lead to several disorders and could be pre-disposing factor for them . The natural mechanism to counteract the effect of reactive oxygen species is via antioxidant compounds (vitamin C, vitamin E, carotene, uric acid) and enzymes (catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase/reductase). Because of two new tannins, amla ( Emblica officinali) have a very strong antioxidant action. The two emblicanins A and B have been found to preserve erythrocytes against oxidative stress induced by asbestos, generator of superoxide radical. Emblicanin A oxidates when put in contact with asbestos becoming emblicanin B and together they have a stronger protective action to erythrocytes than vitamin C. Moreover they improve the efficacy of vitamin C in reducing dihydroascorbic acid to ascorbic acid. The same recycling process has been observed in the rutin- vitamin C combination. Antioxidant compounds can help to protect DNA from the damage associated with free radicals which are highly reactive compounds.
Amla ( Emblica officinali) is effective broad spectrum antioxidants and free radical scavengers, helping to reduce disease and slow the aging process. These compounds in herbs have the capacities to quench lipid peroxidation, prevent oxidative DNA damage, and scavenge ROS, such as superoxide, hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals.
Effect on immune modulation and immune response
Immunity is a homeostatic process, a series of delicately balanced complex, multicellular and physiologic mechanisms that allow an individual to distinguish foreign material from “self” and neutralize and/or eliminate the foreign matter. The immune system is primarily concerned with resistance against foreign invaders and protection against neoplastic cells. Whereas, immunomodulator is an agent that intensifies or diminishes the immune responses and such effect is called as immunomodulatory effect. Immunomodulation using medicinal plants could provide an alternative to conventional chemotherapy for a variety of diseases, especially when host defence mechanism has to be activated under the conditions of impaired immune response or when a selective immunosuppression is desired in situations like autoimmune disorders. Amla ( Emblica officinali) acts as strong immunity booster, antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral medical studies conducted on amla fruit suggest that it has antiviral properties and also functions as an antibacterial and anti- fungal agent. Amla fruit powder as feed additive has been reported to possess antistress, adaptogenic, immunogenic and growthstimulating properties resulting in better performance of broiler.
Antimicrobial effects
Herbal growth promoters due to their multidirectional actions are also useful in controlling pathogenic bacteria without possibility of development of resistance and are also safe for animals and humans. In such manner they can work as herbal antimicrobial agents with other advantages like more economical, free from possibility of resistance, maintaining normal functions, improving production performance in broilers, improving egg size, lymphocyte percentage and egg weight in layers. Aqueous infusion and decoction of amla exhibited potent antimicrobial activity against different strains of Staphylococcus aureus, S. haemolyticus, S.saprophyticus, Micrococccus varians, M. lylae, M. roseus, M. halobius, M. sedenterius, Bacillus subtilis, B. megaterium and Candida albicans.
A study was conducted on phytochemistry and antibacterial activity of Amla phenolic extract against Staphylococcus aureus, Proteus spp., Escherichia coli and Bacillus spp., these strains were obtained from zoonosis research unit of Veterinary Medicine College of Baghdad University. The Emblica officinalis phenolic extract was prepared from dried fruit of Emblica officinalis. Results showed antibacterial activity of Emblica officinalis extract against Staphaureus, Proteus spp., Escherichia coli and Bacillus spp., isolates at different concentrations. The highest inhibition zone for S. aureus bacteria ranged from 16±0.57 to 33.3±0.3 at 10 mg/ml towards 100 mg/ml concentrations respectively in comparison with inhibition zones which were recorded for Bacillus spp., 11.3±0.6 mm to 28±0.06 mm, Escherichia coli 10.6±1.2 to 22.6±1.2 mm and Proteus spp.8.2±0.1 to 20.3±0.57 at same concentrations. Emblica officinalis extract was more effective against all bacteria used in the current study and can be used to treat infections caused by these pathogens after suitable clinical trials.
Anticoccidial effects
Emblica officinalis derived tannins has efficacy on humoral immune responses and has protective efficacy against Eimeria infection in chickens. Tannins were extracted from Emblica officinalis dried fruit . Emblica officinalis derived tannins and commercial tannins were orally administered in broiler chicks in graded doses for three consecutive days, that is, 5th-7th days of age. On day 14 after administration of tannins, humoral immune response was detected against sheep red blood cells by haemagglutination assay. Protective efficacy of tannins was measured against coccidial infection, induced by Eimeria species. Results revealed higher geomean titers against sheep red blood cells in chickens administered with Emblica officinalis tannins as compared to those administered with commercial tannins and control group. Mean oocysts per gram of droppings were significantly lower (P < 0.05) in Emblica officinalis tannins administered chickens as compared to control group. Lesion scoring also showed the lowest caecal and intestinal lesion score of mild to moderate intensity in chickens administered with Emblica officinalis tannins. Further, significantly higher (P < 0.05) daily body weight gains and antibody titers were detected in Emblica officinalis tannins administered chickens as compared to those of commercial tannins administered and control groups. Emblica officinalis tannins showed the immunostimulatory properties in broilers and their administration in chickens boost the protective immunity against coccidiosis.
Usage trend in feed addtives
Amla has various medicinal applications,It has variety of phytochemical such as tannins, flavonoids, terpenoids and alkaloids,These compounds have been indicated several pharmacological properties such as carminative, digestive, stomachic, laxative, antioxidant, antimicrobial and anticoccidial effects. It is considered to be safe herbal feed additives without any adverse effects.Proper use of amla as phytogenic feed additive will be efficient for poultry and livestock production. It will be a good growth promoter for animals.
- Prev:Pomegranate,Punica granatum,Antibacterial,Anticoccidial effect in livestock and poultry
- Next:Medicinal herb Pulsatilla,Antibacterial,Anticoccidiosis,Anti diarrhea,Immune stimulator











