- Plant-Based Protein
- Natural Plant Flavours
- Food and Dietary Supplement Ingredients
- Fruit Juice Powder
- Animal Nutrition Ingredients
- Water Soluble Ingredients
- Cosmetic Ingredients
- Unveiling the Therapeutic Potential of Rabdosia Rubescens: A Comprehensive Review
- What are the medicinal properties of Rabdosia Rubescens?
- Nutritional value of Orange Juice Powder compared to fresh orange juice.
- Processing Conditions and Nutritional Value of Orange Juice Powder
- Exploring the Versatility of Herbal Extracts in Food Flavors

What are the health benefits of hawthorn leaf?
Welcome to our blog! Today, we are diving into the world of hawthorn leaf and uncovering its incredible health benefits. Whether you're a fan of herbal remedies or simply curious about natural alternatives, hawthorn leaf is definitely worth exploring.

Natural Genistein and benefits,dosage,Anti-Cancer, Phytoestrogen
Genistein inhibits protein-tyrosine kinase and topoisomerase-II activity and is used as an antineoplastic and antitumor agent. It has been shown to induce G2 phase arrest in human cell lines.Genistein is a phytoestrogen which has selective estrogen receptor modulator properties. It has been investigated in clinical trials as an alternative to classical hormone therapy to help prevent cardiovascular disease in postmenopausal women. Genistein has been studied as a substitute for hormone replacement therapy. It has shown some promise for treating symptoms that occur early in menopause, such as hot flashes, as well as for problems that occur later, such as osteoporosis.
What you may get from us: If you're developing a product that contains Genistein. You can find the information or products you need here.
Simple production process in our factory: First of all, Sophora japonica was extracted by ethanol and concentrated, and then Sophoricoside was separated and purified to a relatively high purity, and then acid hydrolysis was carried out to get crude genistein. Purify the product with high purity by recrystallization.
How to use Genistein powder: What you need is just use our products to formulate your products. It can be mixed with your other ingredients directly to make premix products. It can also be directly used for filling capsules or making tablets. Easy to say, our products are ready for Formula products.
|
Natural Genistein |
||
|
CAS No. |
446-72-0 |
|
|
Appearance |
Powder |
|
|
Color |
White |
|
|
Partical size |
Normally pass through 80mesh |
|
|
Pack size |
25 kg per paper drum |
|
|
Purity of active compunds |
98% |
By HPLC |
|
For pricing or more information, please call 86 29 88444632 or send an email to Sales@nutraherbsource.com. |
||
General Information
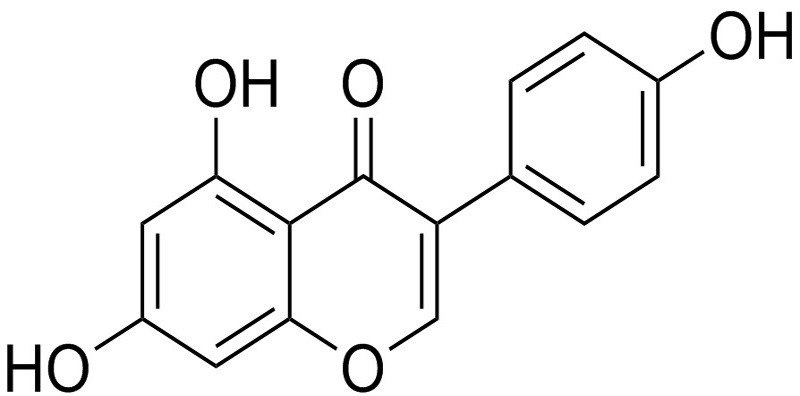
Common Names: 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one, Prunetol,4',5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone, Genisteol.
|
Chemical formula: |
C5H10O5 |
|
Molecular Weight: |
270.24 g/mol |
Physical and chemical property
Gensitein (4', 5, 7-trihydroxyisoflavone) is a heterocyclic diphenol with three hydroxyl groups and its chemical name is 4',5,7-trihydroxy-isofavonethe or 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one. Genistein is a lipophilic compound and has low molecular weight. It showed low aqueous solubility in water. Genistein is thermodynamically and chemically stable and its antioxidant activity sustains for more than 20 days at pH= 7 at 70 °C.
Phytoestrogen Properties:
Phytoestrogens are naturally occurring phenolic plant compounds classified as flavones, isoflavones, coumestans and lignans. Biochemically, phytoestrogens are heterocyclic phenols with a structural similarity to estrogenic steroids (mammalian endogenous estrogens) and therefore, these compounds display estrogen-like activity or weak antiestrogen-like properties. Genistein is an isoflavone and a sub-class of large phenolic constituents of plant secondary metabolites, which shares the typical carbon skeleton of C6–C3–C6, but the phenyl substituent is linked to position 3 instead of position 2, as occurs in the flavan and flavone skeleton. The structure of genistein resembles the 17-β-estradiol estrogen hormone and has various agonistic and antagonistic interactions with estrogens receptors.
Health Benefits of Genistein
In vitro antitumor effect of genistein on prostate cancer.
Physiological concentrations of the soy-derived isoflavone genistein were shown to downregulate the androgen receptor of prostate cancer cells via the estrogen receptor β, resulting in a modified response to hormonal stimuli.They also inhibit several steroid-metabolizing enzymes such as 5-α-reductase or aromatase.It has been postulated that these activities may be protective for prostate cancer by creating a more favorable hormonal milieu. Isoflavones have been well analyzed in human prostate cancer cells over the past years. Genistein inhibited the growth and induced apoptosis in LNCaP, DU-145 and PC3 prostatic cancer cells in a concentration ⩽20 μM. Genistein blocked the cell cycle progression at G1, inhibited PSA expression and modulated cell cycle gene regulation.Expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase, c-myc mRNA and the MDM2 oncogene were downregulated by genistein, whereas p21 mRNA increased in response to genistein in prostate cancer cells DU-145 and LNCaP. Genistein inhibited endothelial cell proliferation and in vitro angiogenesis associated with cancer progression at concentrations of 5 and 150 μM. Further, it was demonstrated that genistein interfered with apoptosis signal transduction by downregulating Bcl-XL expression. Genistein inhibited the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation via the AKT signaling pathway and induced apoptosis in androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cell line LNCaP and the androgen-insensitive cell line PC3 in a concentration of 50 μM, whereas no apoptosis was seen in nontumorigenic CRL-2221 human prostate epithelial cells under genistein treatment. The AKT signaling pathway is an important survival pathway in cellular transduction activated by various growth factors like the epidermal growth factor. AKT also regulates the NF-κB activation. NF-κB activity was completely abrogated in cells pretreated with genistein.
In vitro antitumor effect of genistein on other cancer.
Furthermore, the effects of genistein on PC3 cancer cells and experimental PC3 bone tumors were evaluated by injecting these cells into human bone fragments previously implanted in immunodeficient (severe combined immunodeficiency, SCID) mice. Genistein significantly inhibited PC3 bone tumor growth by regulating the expression of multiple genes involved in the control of cell growth, apoptosis and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo. For example, the expression of various metalloproteinases (MMPs) in PC3 bone tumors was inhibited by genistein treatment, whereas osteoprotegerin was upregulated. MMP immunostaining and transfection experiments also demonstrated inhibition of MMP-9 expression in PC3 cells in vitro and PC3 bone tumors in vivo after genistein treatment.
Estrogen-like properties and benefit for osteoporosis.
Based on its estrogen-like properties, genistein has been studied as a substitute for hormone replacement therapy. It has shown some promise for treating symptoms that occur early in menopause, such as hot flashes, as well as for problems that occur later, such as osteoporosis.
A study published in 2007 in the prestigious Annals of Internal Medicine confirms earlier research regarding genistein’s benefits for osteoporosis. In this double-blind trial, 389 postmenopausal women with mildly reduced bone density were first put on a low-soy diet for four weeks to make sure they didn’t have any genistein in their system. Participants were then given either placebo or 54 mg of genistein daily for 24 months. In addition, all participants were given calcium and vitamin D.After evaluated the bone density in the hip and spine. The results were quite positive. At the end of the study, bone density had increased in participants given genistein, while it decreased in those given placebo; furthermore, this difference was statistically significant. As an additional plus, genistein did not produce the typical, and harmful, estrogen-like effects on the uterus.
What is the association between genistein intake and breast cancer risk?
In in vitro studies
In vitro studies have shown that the growth of both estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells and estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells is inhibited when high levels of genistein (>10µM) are added to the culture medium; however, the growth of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells is actually stimulated when low and physiologically relevant concentrations of genistein are added. The association between genistein and breast cancer risk in vitro is complex and depends on both the concentration of genistein and the concentration of estrogen.
In in vivo studies
Genistein is the most studied of the phytoestrogens in in vivo studies and thus far, rodent studies of genistein and breast cancer risk have had conflicting results. Some studies have shown that genistein inhibits the development and growth of mammary tumors, while other studies have found that genistein stimulates the growth of existing estrogen-sensitive mammary tumors. Evidence indicates that the timing of exposure may be important. Genistein has consistently been shown to inhibit the development of estrogen-sensitive mammary tumors when given to prepubertal rats. Genistein has also been shown to accelerate mammary gland development as well as alter mammary gland development following early life exposure (exposures that took place before or around the time of birth or around the time of puberty) in rat models. Effects depend on time and route of exposure.
Therapeutic Dosages
The optimum dosage of genistein is unknown. In Asia, population groups who eat soy foods daily containing 20 mg to 80 mg of genistein have lower rates of breast and prostate cancer than do groups in the West with less genistein in their diets.
Natural VS Synthetic
At present, there are two sources of genistein on the market: chemical synthesis and natural plants origin. However, there is no evidence to prove whether there is too much difference in physiological activity between the two. Nutra herb ingredients Inc. provides you with natural plant derived genistein.
- Prev:Black elderberry Extract and benefits,side effect COVID-19
- Next:Grape Seed Extract (OPC) and benefits,side effect, uses,dosage,Natural Anti-Oxidant











